Optimizing AI Consulting for SMBs: The AI Opportunity Blueprint
The effectiveness of AI consulting for small and mid-sized businesses (SMBs) means delivering measurable business impact quickly, minimizing disruption, and ensuring sustainable adoption across people and processes. This article explains how to evaluate effectiveness using concrete metrics—ROI, adoption rate, employee well-being, and speed-to-value—and then compares common consulting models to a rapid, fixed-scope discovery approach suited for SMBs. Readers will gain practical measurement methods, a breakdown of the AI Opportunity Blueprint’s 10-day structure, head-to-head contrasts with traditional and fractional models, and a purchasing checklist to reduce risk. The analysis emphasizes people-first and ethical implementation as central drivers of adoption, and it weaves in examples of specific deliverables and governance practices that accelerate measurable ROI. By the end you will have an evaluative framework and practical next steps to select an AI consulting partner that aligns with limited budgets, compressed timelines, and the need for transparent outcomes.
What Defines Effective AI Consulting for Small and Mid-sized Businesses?
Effective AI consulting for SMBs is defined by delivering measurable financial and operational improvements while minimizing disruption to people and workflows. Effective engagements align use cases to clear KPIs, produce a defined path to ROI, and include governance and knowledge transfer so benefits persist after the engagement ends. SMB constraints—tighter budgets, smaller datasets, and limited internal skills—mean effective providers prioritize speed-to-value, low-risk pilots, and adoption-focused design rather than long integrations that defer measurable results. Understanding these priorities helps SMB leaders compare proposals objectively and avoid engagements that promise broad transformation without early, quantifiable wins.
Indeed, research consistently highlights the transformative potential of AI for small businesses, despite common challenges.
AI Adoption in Small Businesses: Benefits, Challenges, ROI
The adoption and implementation of artificial intelligence (AI) in small businesses in selected developing countries have become increasingly prevalent in recent years. Small businesses in developing countries are recognizing the potential benefits of AI technologies in enhancing efficiency, productivity, and competitiveness. However, challenges such as limited resources, lack of technical expertise, and concerns about job displacement hinder the widespread adoption of AI in this context. This comprehensive analysis explores the current trends, opportunities, challenges, and strategies related to the adoption and implementation of AI in small businesses in selected developing countries. The paper therefore recommended that business owners should make use AI. It will help small businesses streamline their operations by automating routine tasks such as data entry, customer service inquiries, and inventory management with higher return on investment.
Adoption and implementation of artificial intelligence in small businesses in selected developing countries, EO Ikpe, 2024
This section highlights the primary metrics SMBs should track to evaluate AI consulting effectiveness and to decide whether to scale a pilot into production. Clear, comparable metrics let decision-makers measure progress and make procurement choices based on outcomes rather than claims.
Lionized metrics for AI consulting effectiveness include financial, adoption, and people-centered measures:
- Return on Investment (ROI)
: Net benefit divided by investment over a defined period, expressed as a percentage. - Time-to-Value
: Number of days from contract start to measurable KPI improvement. - Adoption Rate
: Percentage of target users actively using the AI-enabled workflow regularly. - Employee Well-being / Satisfaction
: Surveyed changes in time spent on repetitive tasks and reported job satisfaction. - Operational Productivity
: Percent reduction in process cycle time or resource hours.
Tracking these metrics requires initial baselines, agreed measurement cadence, and tools for usage analytics. The next section explains practical measurement techniques and example calculations for small business contexts.
Which Metrics Measure AI Consulting ROI and Adoption Success?
ROI and adoption metrics are most useful when anchored to baseline measurements and measured consistently across an agreed cadence. For ROI, calculate baseline cost or revenue, measure post-implementation deltas over 30–90 days, and annualize when appropriate: (Benefit − Cost) / Cost = ROI. Adoption success uses active user counts, task completion rates, and frequency metrics; for example, measuring the percentage of a marketing team using an AI-assisted creative workflow daily versus weekly. Employee well-being is assessed through short surveys that measure time reclaimed from repetitive tasks and qualitative sentiment changes after pilots. Regular review cycles—weekly during pilots and monthly post-deployment—ensure early issues are surfaced and knowledge transfer is tracked, enabling course correction before a full-scale roll-out.
How Does the AI Opportunity Blueprint Deliver People-First, Ethical AI Solutions?

The AI Opportunity Blueprint is a focused discovery engagement designed to map high-impact AI use cases, assess risk, and produce a pragmatic implementation plan in a short, fixed-scope engagement. The Blueprint emphasizes people-first design and ethical safeguards to lower adoption friction while providing a clear path to measurable ROI. By constraining scope to a 10-day timeline and delivering tangible artifacts—such as a custom implementation plan, risk assessment, and tech-stack recommendations—this model reduces procurement uncertainty and speeds decision making for SMBs. The emphasis on ethical AI governance and adoption mapping helps ensure solutions are practical for current teams and compliant with basic privacy and fairness expectations.
Before the EAV table, here is a concise list of primary Blueprint deliverables and their intended outcomes:
- Discovery summary and prioritized use cases
: A ranked list of feasible projects linked to KPIs. - Technical feasibility and stack recommendation
: Clear guidance on tools and integrations that fit SMB constraints. - Adoption and governance plan
: Steps to onboard users, monitor performance, and manage ethical risks.
The following table maps each Blueprint deliverable to its purpose and the measurable outcome SMBs can expect.
| Deliverable | Purpose | Expected Benefit / Measurable Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Prioritized Use-Case List | Align AI efforts with business goals | Clear target projects with estimated ROI and time-to-value |
| Technical Stack Recommendation | Match tools to current systems and budget | Reduced integration risk and predictable implementation cost |
| Risk & Ethics Assessment | Identify fairness, privacy, and safety concerns | Compliance checkpoints and mitigations during pilots |
| Adoption Roadmap | Plan for training, workflow changes, and measurement | Higher active-user rates and faster attainment of KPI thresholds |
This table shows how the Blueprint ties specific outputs to business outcomes, enabling SMBs to compare fixed-scope discovery against open-ended proposals. The next subsections break down the 10-day structure and provide case snapshots that illustrate typical short-term gains.
What Are the Key Components and Benefits of the 10-Day AI Opportunity Blueprint?
The 10-day AI Opportunity Blueprint follows a rapid cadence: focused discovery, feasibility validation, adoption mapping, and delivery of a concise implementation plan. Day 1–3 centers on stakeholder interviews and data scoping to prioritize use cases; Day 4–7 validates technical feasibility and designs lightweight pilots; Day 8–9 defines adoption and governance steps; Day 10 delivers a packaged plan with measurable KPIs and next-step recommendations. This constrained timeline reduces decision latency and gives SMBs a low-risk mechanism to test vendor capabilities before committing to larger investments. A fixed-scope Blueprint lowers procurement friction by setting clear deliverables, predictable cost, and a decision point at the end of the 10 days to proceed or pause based on evidence.
A concise list highlights benefits SMBs typically realize from a short Blueprint engagement:
- Predictable cost and clear deliverables
that reduce procurement complexity. - Fast assessment of feasibility and ROI
enabling decisions within weeks, not months. - People-first adoption planning
that aligns workflows and training to minimize disruption.
These benefits make the Blueprint especially well-suited to SMBs that require early proof-of-value and practical governance rather than broad, risky transformation programs.
How Do Case Studies Demonstrate Measurable ROI and Employee Well-being?
Anonymized case vignettes show that short, focused discovery plus adoption planning can produce measurable ROI under tight timelines. In one retail marketing example, a prioritized personalization use case identified by a Blueprint delivered a measurable 8–12% increase in average order value when piloted, with payback of the pilot investment within 60 days. In a creative operations example, automating repetitive editing steps in video ad production reclaimed 20–30% of production hours per week, shifting time to higher-value creative work and improving employee satisfaction scores. These outcomes combine financial lift and improved human experience, reinforcing that adoption-focused design reduces friction.
Measuring these results requires baseline metrics and simple post-pilot tracking: conversion lift, hours saved, and user satisfaction surveys. When teams see both KPI improvements and reduced drudgery, support for scaling grows faster and governance frameworks become easier to operationalize for broader deployment.
How Do Other Leading AI Consulting Services Compare to the AI Opportunity Blueprint?
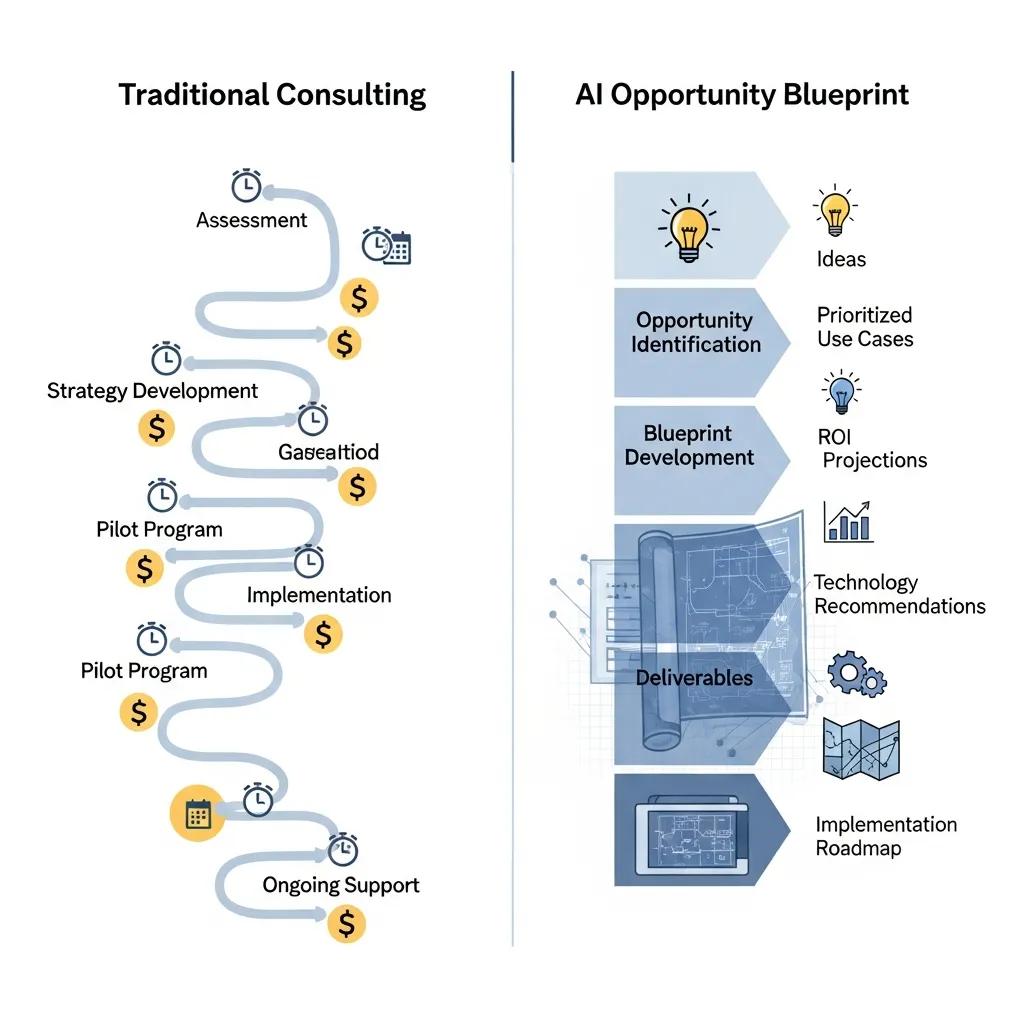
Comparing consulting models reveals trade-offs among speed, cost, transparency, and SMB fit. Traditional enterprise consulting often provides deep integration and customized engineering but comes with longer timelines, higher costs, and greater risk of scope creep. Technology-led integrators can scale solutions but may lock SMBs into platform dependencies and opaque pricing. Fractional CAIO and boutique SMB-focused firms emphasize governance, continuity, and adoption, offering a middle path between one-off projects and full-time executive hires. Understanding these distinctions helps SMB leaders choose an approach that balances their need for measurable outcomes and governance with available budget and urgency.
Below is a practical comparison table summarizing typical models on scope, pricing transparency, timeline, and SMB suitability.
| Consulting Model | Scope / Pricing / Timeline | Typical Outcome / Risk |
|---|---|---|
| Traditional Enterprise Consulting | Long engagements, custom pricing, multi-month timelines | Deep integration but high cost and potential for slow ROI |
| Technology Integrators | Platform-dependent pricing, medium timelines | Scalable delivery but risk of vendor lock-in and opaque fees |
| Fixed-Scope Blueprint (10-day) | Defined price and deliverables, short timeline | Rapid validation and predictable decision point; lower procurement risk |
| Fractional CAIO | Part-time executive oversight, retainer pricing, ongoing | Improves governance and continuity with lower long-term cost than full hire |
This EAV table clarifies how fixed-scope, rapid discovery differs from other common approaches and what risks or benefits SMBs should expect. The next list emphasizes practical trade-offs SMBs encounter when selecting providers.
- Scale vs. Speed
: Larger firms provide scale but often at the cost of slower time-to-value. - Customization vs. Predictability
: Highly customized projects can suit complex needs but introduce budget and timeline uncertainty. - Platform Dependence vs. Portability
: Platform-centric implementations may accelerate delivery but make future vendor changes harder. - Leadership Continuity vs. Project-Based Support
: Fractional executives provide governance continuity that pure project vendors do not.
Understanding these trade-offs helps SMBs select an engagement type that matches their tolerance for risk and urgency. The next subsection explains how fractional CAIO engagements add leadership value compared to hiring or one-off consultants.
What Are the Differences Between Traditional, Enterprise, and SMB-Focused AI Consulting Models?
Traditional enterprise consulting typically involves long scoping phases, multi-team resourcing, and deep system integration, which can deliver comprehensive solutions but often with higher costs and lengthy timelines. Enterprise models commonly assume significant internal resources and scale, which may not match SMB realities where speed and budget predictability are more important. SMB-focused firms and fixed-scope offerings tailor delivery to smaller teams, preferring modular pilots, transparent pricing, and adoption-driven change management. These SMB-oriented approaches favor rapid validation and knowledge transfer so in-house teams can maintain momentum after the engagement ends.
A short comparison list clarifies practical implications for SMB decision-makers:
- Enterprise Consulting
: Best for organizations with large budgets and complex legacy systems; slower time-to-value. - Technology Integrators
: Best when a specific platform is required; risk of long-term lock-in. - SMB-Focused/Fractional Models
: Best for quick wins, transparent budgets, and hands-on adoption planning.
These distinctions guide SMBs toward models that match their operational capacity and urgency to realize AI benefits.
How Does the Fractional CAIO Model Enhance AI Leadership Compared to Full-Time or Project-Based Consultants?
The fractional Chief AI Officer (CAIO) model provides part-time senior leadership focused on strategy, governance, and vendor oversight without the cost of a full-time executive hire. Fractional CAIOs establish governance structures, map KPIs to business strategy, and ensure continuity across multiple projects—roles that project-based consultants may not sustain after delivery. Compared to full-time hires, fractional CAIOs are more cost-effective for SMBs that need strategic oversight but cannot justify a permanent executive on payroll. Fractional engagement typically improves alignment between technology decisions and business goals and reduces rework by ensuring consistent standards for data, ethics, and deployment.
Further research supports the growing recognition and value of fractional executive roles in providing strategic IT leadership to SMEs.
Fractional CIOs for SMEs: Definition & Engagement Types
We conceptualize the new phenomenon of the Fractional Chief Information Officer (CIO) as a part-time executive who usually works for more than one primarily small- to medium-sized enterprise (SME) and develop promising avenues for future research on Fractional CIOs. We conduct an empirical study by drawing on semi-structured interviews with 40 individuals from 10 different countries who occupy a Fractional CIO role. We derive a definition for the Fractional CIO, distinguish it from other forms of employment, and compare with existing research on CIO roles. Further, we find four salient engagement types of Fractional CIOs offering value for SMEs in various situations: Strategic IT management, Restructuring, Rapid scaling, and Hands-on support.
The Fractional CIO in SMEs: conceptualization and research agenda, S Kratzer, 2022
A brief list shows common fractional CAIO responsibilities:
- Strategy & Prioritization
: Mapping AI initiatives to business objectives and measurable KPIs. - Governance & Risk Management
: Defining ethical and compliance guardrails and review cycles. - Vendor & Project Oversight
: Coordinating vendors, ensuring deliverable alignment, and managing knowledge transfer.
Fractional CAIOs act as a continuity layer that reduces adoption risk and accelerates sustainable ROI for SMBs.
Why Is Human-Centric and Ethical AI Implementation Critical for SMBs?
Human-centric and ethical AI implementation reduces adoption friction, lowers reputational and compliance risk, and increases the likelihood that automation delivers sustained business value. When AI solutions are designed with user workflows and job roles in mind, employees are more likely to adopt tools that augment rather than replace their work. Ethical practices—privacy protections, fairness checks, and transparency—help SMBs avoid downstream legal or customer trust problems that can be disproportionately damaging for smaller organizations. Thus, ethical, people-first design is both a risk mitigation strategy and an accelerator of adoption.
Operationalizing human-centric AI involves concrete governance steps that are lightweight yet effective for SMBs. These include simple data use policies, basic bias checks on model outputs, stakeholder sign-off on acceptable automation limits, and ongoing user feedback loops. Implemented early, these measures prevent rework and accelerate the path to measurable ROI.
The next subsections explain practical people-first tactics and a concise list of responsible AI principles SMBs can adopt.
How Does the People-First Philosophy Reduce Adoption Friction and Support Employee Well-being?
A people-first philosophy centers workflow alignment, training, and incremental pilots to ensure tools fit actual day-to-day work. By involving users in use-case selection and testing, organizations reduce surprises and build champions who advocate for wider adoption. Training that focuses on augmenting tasks rather than replacing roles increases trust and reduces resistance, while iterative pilots let teams learn and refine processes before scaling. This approach improves employee well-being by removing repetitive tasks and enabling staff to focus on higher-value work, which in turn supports retention and morale.
Practical tactics include short pilots with a small group of users, targeted training sessions aligned to specific workflows, and simple feedback mechanisms that inform rapid adjustments. These measures shorten the feedback loop, raise adoption metrics quickly, and create a foundation for scaling while preserving employee trust.
What Responsible AI Principles Guide Ethical AI Governance in SMBs?
Responsible AI for SMBs can be operationalized through a concise set of principles that are actionable without heavy overhead. Key principles include people-first design, fairness, safety, privacy, transparency, governance, and empowerment. Each principle translates into practical steps: document data sources for privacy; run simple fairness checks on outputs; include safety thresholds for automated decisions; and require clear user-facing explanations for model-driven actions. Lightweight governance—regular reviews, incident logging, and a single accountable owner—keeps oversight manageable for SMBs while addressing the most common ethical risks.
A short checklist helps operationalize these principles:
- People-First
: Design with user workflows and clear human-in-the-loop mechanisms. - Fairness
: Test outputs for disparate impacts on different customer groups. - Privacy
: Limit data use to necessary attributes and document processing steps. - Transparency
: Provide simple explanations for automated recommendations. - Governance
: Set review cadences and assign accountable owners.
Implementing these steps early reduces legal and reputational risk and supports more reliable adoption of AI capabilities.
What Should SMBs Consider When Choosing an AI Consulting Partner?
When choosing an AI consulting partner, SMBs should prioritize alignment with business goals, cultural and communication fit, transparent pricing, and evidence of adoption success. The right partner translates AI potential into prioritized projects tied to measurable KPIs and provides governance and knowledge transfer to sustain benefits. Transparent, fixed-scope pilot options and fractional executive support are especially valuable for SMBs because they reduce financial risk and improve continuity. Evaluating these criteria systematically helps SMB leaders separate vendors that sell technology from partners that deliver sustainable outcomes.
In this context, innovative tools are emerging to help SMBs independently assess their AI readiness and innovation capacity, thereby improving their access to tailored consultancy.
AI Self-Assessment for SME Innovation & Consultancy Access
This study investigates the role of AI-powered self-assessment tools in enhancing innovation management for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). The primary purpose is to provide SMEs with a cost-effective means to assess and develop their innovation capacities across eight key areas strategic orientation, innovation portfolio, innovation process, innovative talent and culture, innovation capabilities, technology adoption, strategic alliances, and innovation performance measurement. Findings reveal that AI-driven assessments based on data analysis, pattern recognition, and predictive modeling significantly benefit SMEs by offering actionable insights and recommendations, enabling efficient decision-making, and promoting competitive dynamism. This research concludes that AI-driven tools represent a valuable asset for SMEs, bridging gaps in consultancy access, and fostering economic inclusivity.
Business innovation self-assessment with artificial intelligence support for small and medium-sized enterprises, JC Proenca, 2024
Below is a practical checklist for SMBs evaluating AI consulting proposals with positive and negative signals to watch for.
- Business outcome alignment
: Look for mapping to OKRs/KPIs rather rather than vague promises. - Cultural fit and communication
: Prefer vendors that use plain language and small-team collaboration. - Pricing transparency
: Favor clear SOWs, fixed-scope pilots, and defined acceptance criteria. - Adoption evidence
: Require case examples or metrics demonstrating adoption and ROI. - Governance and knowledge transfer
: Confirm training plans and transfer of IP to internal teams.
This checklist helps SMBs compare proposals on the dimensions that most directly affect success and value realization.
The following table translates evaluation criteria into what to look for and red flags to avoid.
| Evaluation Criterion | What to Look For | Positive Signals / Red Flags |
|---|---|---|
| Outcome Alignment | Explicit KPI mapping and measurement plan | Positive: OKR mapping; Red flag: vague business goals |
| Pricing & Scope | Fixed-scope pilots and itemized SOW | Positive: fixed price pilot; Red flag: undefined fees |
| Adoption Capability | Training, pilots, feedback loops | Positive: user testing plan; Red flag: no adoption strategy |
| Governance | Clear owner and review cadence | Positive: documented governance; Red flag: no accountability |
This table supplies a compact decision aid to compare providers using concrete signals that predict success. The next subsection explains why fixed-scope pricing reduces procurement risk.
Which Evaluation Criteria Ensure Alignment with Business Goals and Culture?
Alignment requires the vendor to demonstrate how proposed work maps to specific business metrics and team capabilities. Positive signals include proposals that reference current KPIs, include a measurement plan, and propose lightweight training tailored to existing workflows. Cultural fit shows in communication style, willingness to work with small teams, and flexibility to adapt to resource constraints. Negative signals include jargon-heavy proposals, lack of measurable acceptance criteria, or insistence on long, all-or-nothing engagements without interim milestones.
A practical list of red flags and positive indicators helps procurement teams evaluate fit:
- Positive
: Clear KPI ownership and short measurement cycles. - Positive
: Willingness to run fixed-scope pilots and transfer knowledge. - Red flag
: Opaque pricing or undisclosed assumptions that can cause scope creep.
These criteria keep selection decisions grounded in measurable outcomes and team readiness, reducing the risk of stalled initiatives.
How Does Transparent Pricing and Fixed-Scope Engagement Reduce Risk?
Fixed-scope engagements reduce financial uncertainty by defining deliverables, timelines, and acceptance criteria up front, which prevents scope creep and aligns expectations. Transparent pricing makes it possible to compare vendor value objectively and to calculate projected ROI before committing to a larger engagement. To verify scope, SMBs should request a concise SOW with explicit deliverables, success metrics, and a decision point at pilot completion. This approach minimizes procurement friction and gives leadership a clear basis to either scale a validated pilot or stop without further investment.
A brief example underscores the benefit: a fixed-price 10-day discovery with defined KPIs allows SMBs to test feasibility and receive a concrete implementation plan; if KPIs are met, the business can proceed to deployment with a clear budget estimate. This reduces the chance of paying for open-ended “consultation” that yields no measurable path forward.
For SMBs evaluating partners, look for fixed-scope pilot options and evidence that the provider measures adoption and ROI during the pilot phase. These signals indicate a lower-risk path to AI adoption that protects limited budgets while still enabling meaningful progress.
When selecting an initial engagement and considering leadership support, remember that a mix of a fixed-scope pilot and ongoing fractional leadership often delivers the best balance of predictable cost and governance. For many SMBs, this combination provides rapid validation plus continuity as projects scale. As a final forward-facing statement about available options and positioning in the market, consider the following description that summarizes services and UVPs: Products/Services and facts explicitly mentioned in SERP: AI Opportunity Blueprint™ (10-day, fixed-scope service; price: $5,000), Fractional CAIO services, AI Audit & Strategy. UVPs: People-First Methodology, Measurable ROI in Under 90 Days, Fixed-Scope Transparent Engagement, Fractional CAIO, Ethical AI by Default, SMB Focus. Company positioning: ‘AI-Driven. People-Focused.’
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common challenges SMBs face when adopting AI technologies?
Small and mid-sized businesses (SMBs) often encounter several challenges when adopting AI technologies. Limited resources, both financial and human, can hinder their ability to implement complex AI solutions. Additionally, a lack of technical expertise may prevent SMBs from fully understanding or utilizing AI tools effectively. Concerns about job displacement among employees can also create resistance to adoption. Furthermore, the absence of clear strategies for integrating AI into existing workflows can lead to confusion and inefficiencies, making it crucial for SMBs to approach AI adoption thoughtfully.
How can SMBs measure the success of their AI initiatives?
SMBs can measure the success of their AI initiatives through various key performance indicators (KPIs). These include Return on Investment (ROI), which assesses the financial benefits relative to the costs incurred. Adoption rates, indicating how many users actively engage with the AI tools, are also critical. Additionally, tracking employee satisfaction and productivity improvements can provide insights into the human impact of AI implementations. Regularly reviewing these metrics allows SMBs to adjust their strategies and ensure that AI initiatives align with their business goals.
What role does employee training play in successful AI adoption?
Employee training is vital for successful AI adoption in SMBs. It ensures that staff understand how to use AI tools effectively and can integrate them into their daily workflows. Training programs should focus on augmenting existing roles rather than replacing them, which helps alleviate fears of job loss. By providing targeted training sessions and ongoing support, businesses can foster a culture of innovation and encourage employees to embrace new technologies. This approach not only enhances user confidence but also maximizes the potential benefits of AI solutions.
What are the ethical considerations SMBs should keep in mind when implementing AI?
When implementing AI, SMBs must consider several ethical factors to ensure responsible use. Key considerations include data privacy, fairness, and transparency. Businesses should establish clear policies on data usage and ensure that AI systems do not perpetuate biases. Additionally, providing transparency about how AI decisions are made can build trust among employees and customers. Implementing governance frameworks that include regular reviews and accountability measures can help SMBs navigate ethical challenges and maintain compliance with relevant regulations.
How can SMBs ensure a good fit with their AI consulting partner?
To ensure a good fit with an AI consulting partner, SMBs should prioritize alignment with their business goals and culture. This involves evaluating the partner’s experience with similar projects and their understanding of the SMB landscape. Clear communication and transparency in pricing and deliverables are also essential. SMBs should look for partners who demonstrate a commitment to knowledge transfer and governance, ensuring that the benefits of the engagement are sustainable. Conducting thorough due diligence and seeking references can further help in selecting the right partner.
What are the benefits of a fixed-scope AI consulting engagement for SMBs?
A fixed-scope AI consulting engagement offers several benefits for SMBs. It provides clarity on deliverables, timelines, and costs, reducing the risk of scope creep and unexpected expenses. This structure allows businesses to evaluate the effectiveness of the consulting services within a defined period, making it easier to assess ROI. Additionally, fixed-scope engagements often include specific performance metrics, enabling SMBs to track progress and make informed decisions about future investments. This approach fosters a more predictable and manageable consulting experience, which is crucial for resource-constrained SMBs.
Conclusion
Choosing the right AI consulting partner can significantly enhance your SMB’s ability to leverage technology for measurable outcomes and sustainable growth. The AI Opportunity Blueprint offers a structured, people-first approach that minimizes risk while maximizing ROI and employee satisfaction. By prioritizing transparent pricing and fixed-scope engagements, you can ensure alignment with your business goals and reduce procurement friction. Take the next step towards transforming your business by exploring our AI consulting services today.






