Unlocking the AI Opportunity Blueprint: Ethical AI Implementation and Governance for SMBs
Introduction
The AI Opportunity Blueprint™ is a practical, time-boxed method that helps small and mid-sized businesses adopt AI responsibly while keeping ethics and people at the center of strategy. This article explains how ethical AI implementation for SMBs reduces legal and reputational risk, accelerates adoption, and improves measurable ROI by aligning governance, process, and workforce enablement. Readers will learn core ethics principles, governance best practices, bias detection and transparency tactics, and a reproducible framework for measuring impact. The piece maps the AI Opportunity Blueprint™ phases, explains human-centric interventions that reduce adoption friction, and outlines governance steps—such as fractional Chief AI Officer oversight—that SMBs can deploy now. Throughout, we reference practical tools and templates SMB leaders can apply to build AI ethics policies and governance that support both compliance and performance.
This strategic imperative for SMBs to embrace ethical AI is further underscored by recent research highlighting the critical role of leadership in navigating AI-driven digital transformation.
Ethical AI Governance & Strategic Adoption for SMEs
This The transformative force of AI-driven digitalization demands a paradigm shift in leadership, one that transcends conventional frameworks to address the complexities of disruptive innovation, ethical governance, and sustainable business strategies. This research critically examines the advanced leadership capabilities required to drive the adoption and integration of frontier technologies—including artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), blockchain, and fintech—within the operational ecosystems of multinational corporations and small-to-medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). Digital transformation is not merely a technologicaltransition but a profound organizational realignment, necessitating leaders with the vision and dexterity to dismantle silos, foster innovation, and institutionalize sustainability as a core strategic objective.
Strategic leadership in AI-driven digital transformation: Ethical governance, innovation management, and sustainable practices for global enterprises and SMEs, 2025
Ethical AI Implementation: A Roadmap for SMB Success
Ethical AI implementation for SMBs means designing systems that minimize bias, protect privacy, and include human oversight so decisions remain accountable and fair. This approach reduces legal exposure and reputational damage while improving adoption because employees and customers trust transparent, well-governed systems. Ethical practices also enable better decision quality and operational efficiency, which directly contributes to the ROI of ethical AI investments. The following list highlights the primary benefits SMBs realize when ethics are prioritized and explains the risks of neglect.
Ethical AI delivers concrete benefits:
- Legal Protection: Clear documentation and impact assessments reduce regulatory risk and support compliance.
- Reputation & Trust: Transparent systems increase customer and partner confidence in automated decisions.
- Workforce Well-Being: Human-centric design lowers adoption friction and reduces employee stress during change.
- Faster ROI: Measurable adoption and efficiency gains accelerate payback, often within months.
These benefits make clear why governance and ethics are foundational; the next section defines core principles to embed into practical policy and day-to-day operations.
What are the core principles of an AI ethics framework for SMBs?
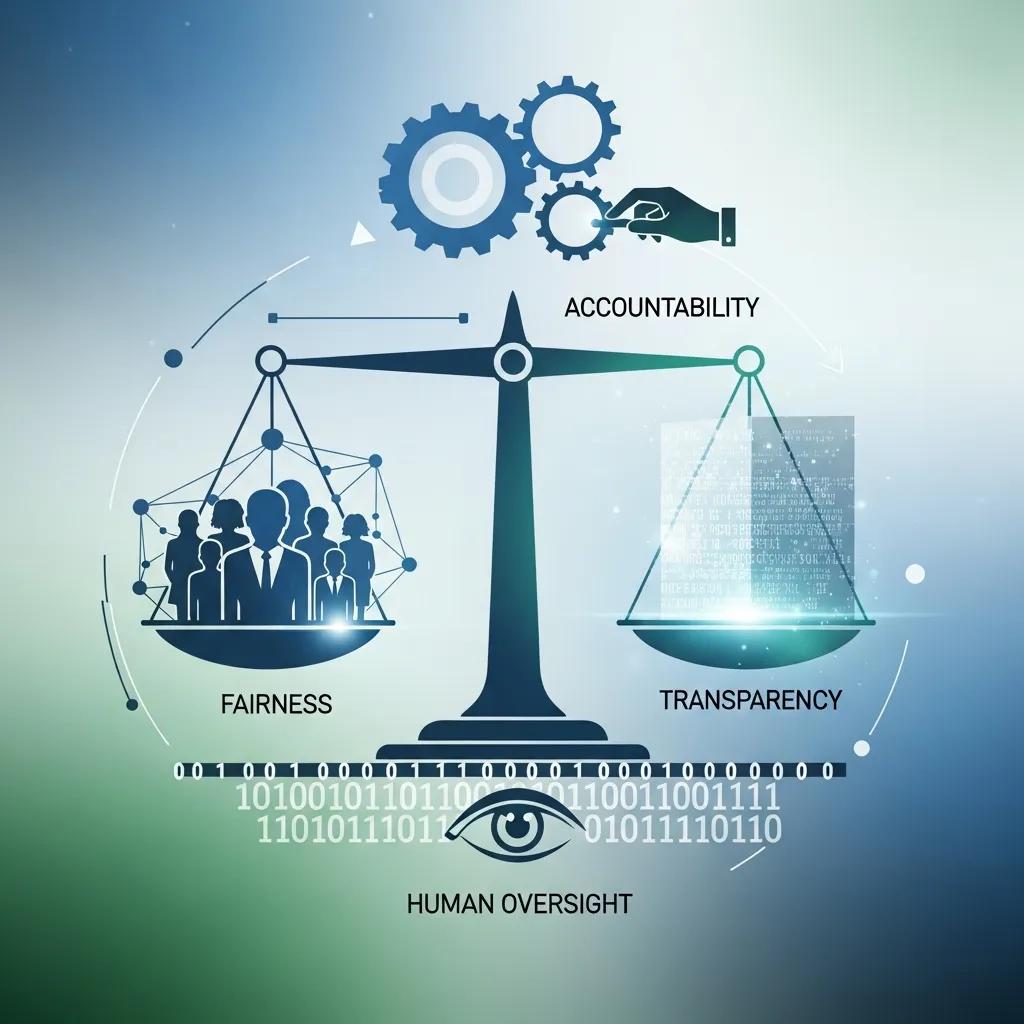
Core principles for an AI ethics policy template for small business include fairness, transparency, accountability, privacy protection, and human oversight. Fairness requires bias mitigation across data and models, implemented through diverse sampling and evaluation metrics that detect disparate impact. Transparency includes documentation like model cards and explainability reports so stakeholders understand how decisions are made and can challenge outcomes. Accountability assigns clear roles—owner, reviewer, and escalation path—so every AI system has responsible governance and measurable controls. These principles yield concrete actions: documented data lineage, periodic fairness audits, privacy-by-design data handling, and clear human-in-the-loop checkpoints that keep automated decisions aligned with business values.
The importance of these core principles is echoed in contemporary research emphasizing the need for robust ethical frameworks to manage bias, ensure fairness, and maintain transparency in AI-powered business intelligence systems.
Ethical AI Frameworks: Bias, Fairness, Transparency & Governance
The ethical implementation of artificial intelligence in business intelligence systems represents a critical intersection of technological advancement and moral responsibility. As organizations increasingly integrate AI-driven decision-making processes, the imperative for robust ethical frameworks becomes paramount. The focus on data quality, fairness mechanisms, and transparency protocols emerges as essential components for building trustworthy AI systems. Organizations face complex challenges in maintaining data integrity while addressing inherent biases that can perpetuate societal inequities. The implementation of comprehensive monitoring systems, coupled with structured governance frameworks, enables businesses to detect and mitigate potential ethical concerns proactively. Through the establishment of clear communication channels and accountability measures, organizations can foster public trust while ensuring compliance with evolving regulatory standards.
The Ethical Backbone of AI-Powered Business Intelligence: Bias, Fairness, and Transparency, 2025
These framework elements naturally lead into how ethical design choices affect strategy and measurable outcomes when operationalized across projects.
How does ethical AI drive business strategy and ROI?
Ethical AI drives strategy by converting trust into adoption, and adoption into measurable performance gains that support business objectives. When SMBs implement transparency and human oversight, employee acceptance increases and deployment cycles shorten, producing earlier benefits such as time saved and reduced error rates. For example, adding explainability can reduce customer service escalations and speed resolution, converting operational savings into higher net promoter scores and retention. The measurable ROI of ethical AI investments often appears as productivity gains, reduced rework, and faster time-to-value, aligning ethics with the bottom line and strategic growth.
Understanding this ROI framework helps justify investments in governance and training, which the AI Opportunity Blueprint™ explicitly operationalizes in its 10-day roadmap described next.
For SMBs seeking a ready-made, ethics-first pathway to AI adoption, the Fort Wayne-based consulting firm eMediaAI—founded by Certified Chief AI Officer Lee Pomerantz—offers a human-centered approach described below; their AI Opportunity Blueprint™ packages governance, readiness assessment, and actionable deliverables into a structured 10-day program that embeds ethics and people-first design.
How Does the AI Opportunity Blueprint™ Facilitate Responsible AI Adoption?
The AI Opportunity Blueprint™ is a 10-day structured roadmap that operationalizes ethical AI adoption by combining readiness assessment, risk analysis, and a prioritized implementation plan. The Blueprint balances people, process, and technology—following a “People-first strategy. Then process. Then tech.” posture—to ensure solutions are practical and adopted by teams. In practice, the Blueprint produces deliverables such as a prioritized AI roadmap, impact and risk assessments, vendor and stack recommendations, and an implementation checklist that ties ethics to measurable KPIs. The program is offered as a focused engagement priced at approximately $5,000 and emphasizes ethical integration at each phase to accelerate measurable ROI, often helping teams realize benefits within 90 days.
The Blueprint breaks adoption into ten compact phases so SMBs can evaluate opportunities, manage risk, and plan rollout efficiently:
- Opportunity Identification: Document candidate use cases and business impact.
- Stakeholder Mapping: Identify owners, users, and escalation paths.
- Data Inventory: Record data sources, quality, and privacy considerations.
- Readiness Assessment: Score technical and organizational readiness.
- Risk & Ethics Assessment: Conduct initial fairness and regulatory risk review.
- Tech Stack Evaluation: Recommend tools and integration paths.
- Proof-of-Concept Design: Define scope, metrics, and success criteria.
- Implementation Roadmap: Create timeline, milestones, and resource plan.
- Training & Enablement Plan: Specify workforce learning and adoption supports.
- Governance Handoff: Deliver policy templates, monitoring plans, and audit checkpoints.
Before the table below, note that the Blueprint is designed to be human-centric and executable within a short timebox, enabling leaders to move from assessment to action rapidly.
Purposeful summary of the Blueprint phases and expected outcomes:
| Phase | Deliverable | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Opportunity Identification | Use case list | Prioritized value drivers |
| Stakeholder Mapping | RACI matrix | Clear ownership |
| Data Inventory | Data catalog | Data readiness visibility |
| Readiness Assessment | Scorecard | Go/no-go clarity |
| Risk & Ethics Assessment | Impact checklist | Mitigation list |
| Tech Stack Evaluation | Tools matrix | Integration plan |
| Proof-of-Concept Design | POC specs | Testable success criteria |
| Implementation Roadmap | Gantt & milestones | Execution timeline |
| Training & Enablement Plan | Curriculum | Faster adoption |
| Governance Handoff | Policy templates | Ongoing oversight |
This EAV (phase | deliverable | outcome) table condenses the Blueprint into a quick-reference format that SMB leaders can use to align resources and track ethical checkpoints through deployment.
The Blueprint’s emphasis on human-centric steps—training, stakeholder mapping, and governance handoffs—creates momentum for adoption while keeping ethical safeguards in place. The next section explains governance patterns SMBs should pair with technical controls to meet regulatory expectations and industry best practices.
What are the 10 key phases of the AI Opportunity Blueprint™?
The ten phases above are designed to move an SMB from idea to governed implementation in practical increments that embed ethics at every stage. Each phase produces tangible outputs—catalogs, scorecards, policy templates, and roadmaps—that become living documentation for audits and continuous improvement. The POC and implementation roadmap phases explicitly include monitoring and explainability requirements so the deployed models remain transparent to users and reviewers. This structured approach reduces common pitfalls like scope creep, undocumented data use, and lack of ownership, and positions teams to measure ROI quickly. By consolidating ethics checks into deliverables, the Blueprint makes regulatory readiness and operational adoption a natural part of delivery rather than an afterthought.
These phase outputs are intentionally concise to help SMBs make decisions and to shorten the timeline from assessment to measurable benefit, which supports the business case for using a structured engagement.
How does the Blueprint integrate human-centric AI principles?
Human-centric integration in the Blueprint prioritizes workforce training, participatory design, and incremental rollouts to reduce adoption friction and protect employee well-being. Training modules address AI literacy at role-relevant depth so users can interpret model outputs and provide meaningful feedback, which improves model calibration and trust. Participatory design sessions capture frontline user concerns and adjust UX to minimize stress and cognitive load, while change-management checklists ensure gradual exposure and measurable satisfaction metrics. Governance handoffs include human-in-the-loop controls and escalation paths, enabling human review for high-risk decisions and preserving accountability.
These interventions convert ethical commitments into operational actions that increase adoption, boost productivity, and accelerate the timeline for realizing ROI from AI investments.
What Are the Best Practices for AI Governance and Compliance in SMBs?

Effective AI governance for SMBs combines clear policy, assigned oversight, continuous monitoring, and audit-ready documentation so teams can scale responsibly without undue complexity. Governance must be proportional: policies should be concise, roles clearly defined, and monitoring automated where feasible to reduce ongoing operational burden. Practical governance supports regulatory preparedness—such as classification of systems, impact assessments, vendor controls, and logging—while preserving agility. The checklist below captures five high-impact governance actions SMBs can implement quickly to align ethics with compliance and business goals.
Start with this five-step governance checklist:
- Define a concise AI policy: State objectives, acceptable uses, and prohibited behaviors.
- Assign oversight: Create a governance owner and review cadence for models and data.
- Implement monitoring: Set automated checks for drift, performance, and fairness.
- Maintain documentation: Keep impact assessments, model cards, and logs for audits.
- Control vendors: Require vendor transparency and contractual data protections.
These steps form a compact governance playbook that prepares SMBs for evolving regulation while enabling operational oversight and continuous improvement.
How can SMBs prepare for AI regulations like the EU AI Act?
Preparing for regulations such as the EU AI Act begins with classifying AI systems by risk level, documenting intended use, and producing impact assessments that demonstrate mitigation strategies. SMBs should inventory systems, map data flows, and collect evidence—model cards, test reports, and logging—that show how privacy, fairness, and safety are managed. Vendor controls and contractual clauses are critical when third-party models or data are included, ensuring accountability flows through supply chains. Establishing a regular audit cadence and keeping concise governance documentation provides the evidence regulators and customers expect while enabling faster remediation when issues arise.
These readiness tasks lead naturally to the question of who provides ongoing leadership; the next subsection covers the fractional Chief AI Officer model as a practical governance alternative for SMBs.
What role does a Fractional Chief AI Officer play in ethical AI leadership?
A Fractional Chief AI Officer (fCAIO) provides strategic leadership, governance oversight, and ethics stewardship without the fixed cost of a full-time executive, making the model attractive to SMBs. The fCAIO responsibilities include defining AI strategy, establishing governance policies, overseeing impact assessments, and coordinating training and change management. Compared to a full-time CAIO, a fractional approach delivers focused expertise on priority initiatives with flexible engagement levels and measurable deliverables. This model accelerates ethical maturity by assigning executive-level accountability, aligning AI programs with business objectives, and ensuring oversight for compliance and risk mitigation.
A short comparison clarifies why SMBs often choose fractional leadership to operationalize ethics while preserving budget flexibility and governance rigor.
| Governance Component | Compliance Action | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Policy & Standards | Create concise AI policy | Clear acceptable uses |
| Oversight & Roles | Assign governance owner/fCAIO | Accountable decision-making |
| Monitoring & Audit | Implement model cards/logging | Audit-readiness |
| Vendor Management | Require vendor transparency | Reduced supply-chain risk |
How Can SMBs Mitigate AI Risks Through Bias Detection and Transparency?
SMBs reduce AI risks by deploying bias detection workflows, model explainability practices, and stakeholder communication templates that make decisions reviewable and contestable. Bias detection involves pre-processing checks for data representativeness, in-processing constraints and fairness-aware algorithms, and post-deployment monitoring using performance and disparity metrics. Transparency practices—model cards, explainability summaries, and user-facing explanations—help stakeholders understand when and how AI influences outcomes. The three tactical strategies below offer concrete starting points for teams that need to mitigate algorithmic bias and increase explainability for customers and regulators.
Three tactical strategies to reduce bias and increase transparency:
- Data Hygiene & Audit: Regularly analyze datasets for representation gaps and apply sampling or augmentation to reduce skew.
- Evaluation & Metrics: Use fairness metrics and subgroup analyses during model validation to detect disparate impacts.
- Explainability & Documentation: Publish model cards and user-facing explanations that clarify decision logic and limitations.
These strategies create a pipeline of checks that detect problems early; the next subsection outlines specific interventions across the model lifecycle.
What strategies reduce algorithmic bias and ensure fairness?
Reducing algorithmic bias requires interventions at three stages: pre-processing (data balancing, anonymization), in-processing (fairness-aware training constraints), and post-processing (score recalibration, human review). Practical tools include data profiling automation to detect distributional imbalances and test suites that evaluate performance across demographic slices. Validation should include both statistical fairness metrics and real-world impact tests that mirror deployment scenarios so teams can observe unintended consequences before release. Incorporating human review for edge or high-risk cases ensures fairness considerations remain contextual and actionable.
Implementing these measures improves model reliability and preserves stakeholder trust, which sets the stage for transparent communication about AI decisions.
How to foster AI transparency and explainability for stakeholders?
Fostering transparency combines technical explainability tools with clear documentation and stakeholder communication templates that translate model behavior into business terms. Model cards summarize purpose, training data characteristics, evaluation metrics, and known limitations; explainability reports provide feature attributions and typical decision examples that non-technical audiences can understand. For user-facing systems, short contextual explanations alongside outputs help affected individuals grasp why a decision was made and how to seek review. Regular stakeholder briefings and accessible documentation build institutional knowledge and create an audit trail that regulators and partners can examine.
Further advancing the field, innovative frameworks are emerging to enhance explainable AI by integrating human-like reasoning and multi-agent collaboration for more transparent and context-aware systems.
Responsible AI Blueprint: Explainability & Human-Centric Systems
This paper introduces System-of-Systems Machine Learning (SoS-ML) as a novel framework to advance explainable artificial intelligence (XAI) by addressing the limitations of current methods. Drawing from insights in philosophy, cognitive science, and social sciences, SoS-ML seeks to integrate human-like reasoning processes into AI, framing explanations as contextual inferences and justifications. The research demonstrates how SoS-ML addresses key challenges in XAI, such as enhancing explanation accuracy and aligning AI reasoning with human cognition. By leveraging a multi-agent, modular design, SoS-ML encourages collaboration among machine learning models, leading to more transparent, context-aware systems. The findings emphasize SoS-ML’s role in advancing responsible AI, particularly in high-stakes environments where interpretability and social accountability are paramount.
Towards responsible AI: an implementable blueprint for integrating explainability and social-cognitive frameworks in AI systems, R Shamsuddin, 2025
Clear explanations and documentation reduce friction and empower stakeholders to use AI outputs responsibly, which supports adoption and mitigates reputational risk.
How Does Human-Centric AI Enhance Employee Well-Being and Adoption?
Human-centric AI enhances employee well-being by designing workflows that augment—not replace—human judgment, which reduces anxiety and increases perceived usefulness. When AI systems include transparent interfaces, human oversight, and role-appropriate training, employees gain confidence and are more likely to adopt tools effectively. Measured outcomes include higher adoption rates, fewer errors, and tangible time savings that free staff for higher-value work. The following list outlines direct benefits of investing in AI literacy and structured workforce enablement programs.
Benefits of AI literacy and workforce training:
- Improved Adoption: Clear training reduces resistance and accelerates use.
- Error Reduction: Users who understand system limits make better decisions.
- Empowerment: Staff gain skills that increase job satisfaction and versatility.
- Faster ROI: Trained teams extract value sooner through efficient workflows.
These benefits motivate structured training and change management as core parts of any deployment plan.
What are the benefits of AI literacy and workforce training?
AI literacy and workforce training increase adoption by equipping staff with the skills to interpret outputs, identify anomalies, and participate in model improvement cycles. Training formats that work well for SMBs include short workshops, role-based microlearning modules, and hands-on POC sessions that let users validate model behavior in context. Empowered users contribute better labeled data, more actionable feedback, and smoother change management, all of which shorten the path to measurable benefits. Well-designed enablement also reduces stress by clarifying human roles and providing explicit escalation paths when automated suggestions conflict with expert judgment.
These training investments produce measurable improvements in usage metrics and overall system performance, which are central to the ROI framework described next.
How does managing AI adoption friction improve productivity and reduce stress?
Managing adoption friction focuses on UX design, incremental rollouts, and feedback loops that limit disruption and allow teams to adapt gradually. A before/after mini-case shows that incremental rollout with embedded review checkpoints reduced error rates and increased task throughput, while full-scope immediate deployment caused confusion and rollback. Suggested metrics to track include time saved per task, error reduction percentage, and employee satisfaction scores collected during pilot phases. Monitoring these KPIs provides early evidence of productivity gains and guides iterative adjustments to training and tooling.
Lowering friction through human-centered practices thus directly translates into better productivity and healthier workplace dynamics, reinforcing the ethical rationale for people-first AI.
What Evidence Demonstrates the ROI of Ethical AI Adoption?
Demonstrable ROI from ethical AI adoption comes from measured reductions in time-to-decision, error rates, and operational costs, combined with improved customer and employee outcomes. SMBs can quantify benefits using simple templates: time saved × hourly rate = labor savings; adoption lift × revenue per user = revenue impact. Short-term KPI targets often show tangible improvements within 30–90 days when governance, training, and a focused implementation plan are in place. The anonymized case summaries below illustrate how ethical design choices produced measurable results across different SMB use cases.
The following EAV-style case summaries show problem, ethical approach, and quantified result for quick assessment:
| Case Study | Ethical Approach | Quantified Result |
|---|---|---|
| E-commerce personalization | Fairness review + explainability | 18% uplift in conversion for underrepresented segments |
| Video ad optimization | Human-in-loop A/B testing + transparency | 22% reduction in wasted ad spend |
| Podcast content tagging | Privacy-first data pipeline + training | 35% time saved in metadata curation |
These anonymized examples underscore that ethical interventions yield measurable business impact in diverse operational contexts and that ROI is not purely theoretical.
Which case studies highlight ethical AI success in SMBs?
An e-commerce firm applied fairness audits and adjusted sampling to reduce biased recommendations; the ethical approach expanded reach and produced an 18% uplift in conversions among previously underrepresented customer segments. A media company implemented human-in-loop ad optimization paired with clear reporting; transparency reduced wasted ad spend by 22% while preserving creative control. A content production team redesigned tagging workflows with privacy-by-design data handling and focused training; the result was a 35% reduction in manual curation time. In each case, ethical design choices directly enabled higher adoption, better business metrics, and defensible decision trails.
These vignettes demonstrate how pairing governance with human-centric practices converts ethical commitments into measurable outcomes.
How to quantify the business impact of responsible AI investments?
Use a simple ROI worksheet to quantify impact: estimate time saved per task, multiply by the number of tasks and average hourly rate to get labor savings; estimate adoption lift as a percentage increase in active users and multiply by revenue per user to calculate incremental revenue. Include cost lines for tool licensing, training, and governance to compute net benefit and payback period. Recommended KPIs to track include time saved, error rate reduction, adoption rate, revenue impact, and regulatory incident reduction. Regular measurement pacing—monthly during pilots and quarterly post-deployment—keeps leadership informed and supports iterative improvements.
Applying this measurement discipline ensures ethical AI initiatives are evaluated by the same financial rigor as other business investments and supports continued scaling.
For SMBs that want a practical, ethics-first path to measurable AI adoption, the AI Opportunity Blueprint™ and fractional Chief AI Officer services can provide structured deliverables, governance, and enablement to accelerate results; eMediaAI’s human-centered approach and productized engagement model are examples of how SMBs can access this expertise without large upfront overhead.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common challenges SMBs face when implementing ethical AI?
Small and mid-sized businesses (SMBs) often encounter several challenges when implementing ethical AI. These include limited resources for training and governance, a lack of understanding of ethical frameworks, and difficulties in integrating AI systems with existing processes. Additionally, SMBs may struggle with data quality and representation, which can lead to biased outcomes. Overcoming these challenges requires a commitment to education, investment in the right tools, and a structured approach to governance that aligns with their business objectives.
How can SMBs ensure ongoing compliance with AI regulations?
To ensure ongoing compliance with AI regulations, SMBs should establish a robust governance framework that includes regular audits, impact assessments, and documentation of AI system performance. This involves classifying AI systems by risk level, maintaining clear records of data usage, and implementing automated monitoring for compliance checks. Additionally, staying informed about evolving regulations and engaging with legal experts can help SMBs adapt their practices proactively, ensuring they meet both current and future regulatory requirements.
What role does employee training play in ethical AI adoption?
Employee training is crucial for the successful adoption of ethical AI in SMBs. It equips staff with the necessary skills to understand AI outputs, recognize potential biases, and engage in model improvement processes. Training programs should be tailored to different roles within the organization, focusing on practical applications and ethical considerations. By fostering AI literacy, businesses can enhance user confidence, reduce resistance to new technologies, and ultimately drive higher adoption rates, leading to better overall performance and ROI.
How can SMBs measure the success of their ethical AI initiatives?
SMBs can measure the success of their ethical AI initiatives by tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) such as time saved, error rates, user adoption rates, and overall business impact. Implementing a structured ROI framework allows businesses to quantify benefits, such as labor savings and revenue increases, directly linked to ethical AI practices. Regularly reviewing these metrics helps organizations assess the effectiveness of their strategies, make informed adjustments, and demonstrate the value of ethical AI to stakeholders.
What are the best practices for fostering a culture of ethical AI in SMBs?
Fostering a culture of ethical AI in SMBs involves several best practices, including promoting transparency in AI decision-making, encouraging open dialogue about ethical concerns, and integrating ethical considerations into all stages of AI development. Leadership should model ethical behavior and provide training that emphasizes the importance of ethics in AI. Additionally, establishing clear policies and governance structures can help reinforce these values, ensuring that all employees understand their role in maintaining ethical standards within the organization.
How can SMBs leverage partnerships to enhance their ethical AI capabilities?
SMBs can enhance their ethical AI capabilities by forming strategic partnerships with technology providers, academic institutions, and industry organizations. Collaborating with experts can provide access to advanced tools, resources, and knowledge that may be otherwise unavailable. These partnerships can also facilitate training opportunities, share best practices, and foster innovation in ethical AI practices. By leveraging external expertise, SMBs can accelerate their ethical AI initiatives and ensure they are aligned with industry standards and regulatory requirements.
Conclusion
Implementing ethical AI practices empowers small and mid-sized businesses to enhance trust, improve operational efficiency, and achieve measurable ROI. By prioritizing governance and human-centric design, SMBs can navigate the complexities of AI adoption while minimizing risks and maximizing benefits. The AI Opportunity Blueprint™ offers a structured pathway to integrate these principles effectively. Discover how our tailored solutions can support your ethical AI journey today.
The ai opportunity blueprint advantages help businesses identify key areas where AI can create value, driving innovation and growth. Embracing this framework allows for the alignment of AI initiatives with organizational goals, ensuring long-term success. As a result, companies can unlock new revenue streams and enhance customer experiences through informed decision-making.






